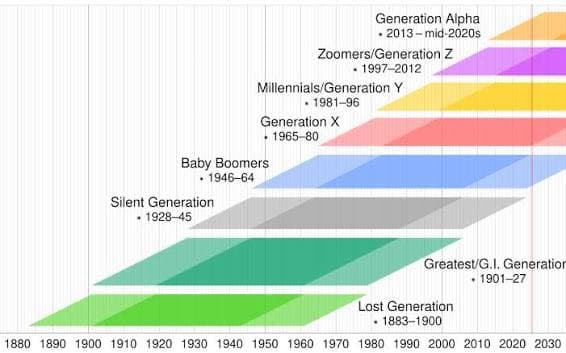
The American electorate is experiencing significant demographic changes, with projections indicating that by 2030, Millennials and Generation Z will comprise approximately 60% of voters. Currently, the Silent Generation and Baby Boomers are seeing a decline in their representation on voter rolls. Each year, an estimated 1.4 to 1.7 million Silent Generation voters and 1.0 to 1.2 million Baby Boomer voters pass away, while up to 2.6 million Gen Z voters are registering annually.
As of now, Baby Boomers make up about 26.5% of the electorate, a decrease from over 30% in 2016 and more than 28% in 2020. This percentage is expected to drop to 22% by 2030. The Silent Generation, known for its conservative voting patterns, is projected to decline from around 9% today to approximately 5% by 2030.
Generation X is also anticipated to see a reduction in their share of the electorate, decreasing from about 24% today to 22.5% by 2030. In contrast, Millennials are expected to increase their representation from around 27.5% to 35%, while Gen Z voters are projected to double their share from approximately 12.5% to 25% by the same year. Neither major political party currently holds a strong influence over Gen Z voters, indicating a shift in the political landscape.
These changes reflect a broader transformation within the American voting population, as younger generations become more prominent in the electoral process.



![[Video] Putin ready to refrain from deep strikes in Ukraine during elections](/_next/image?url=%2Fapi%2Fimage%2Fthumbnails%2Fthumbnail-1766158260919-wednc8-thumbnail.jpg&w=3840&q=75)


![[Video] Gunfire between Iraqi security forces and Sadr militias in Baghdad](/_next/image?url=%2Fapi%2Fimage%2Fthumbnails%2Fthumbnail-1768343508874-4redb-thumbnail.jpg&w=3840&q=75)
