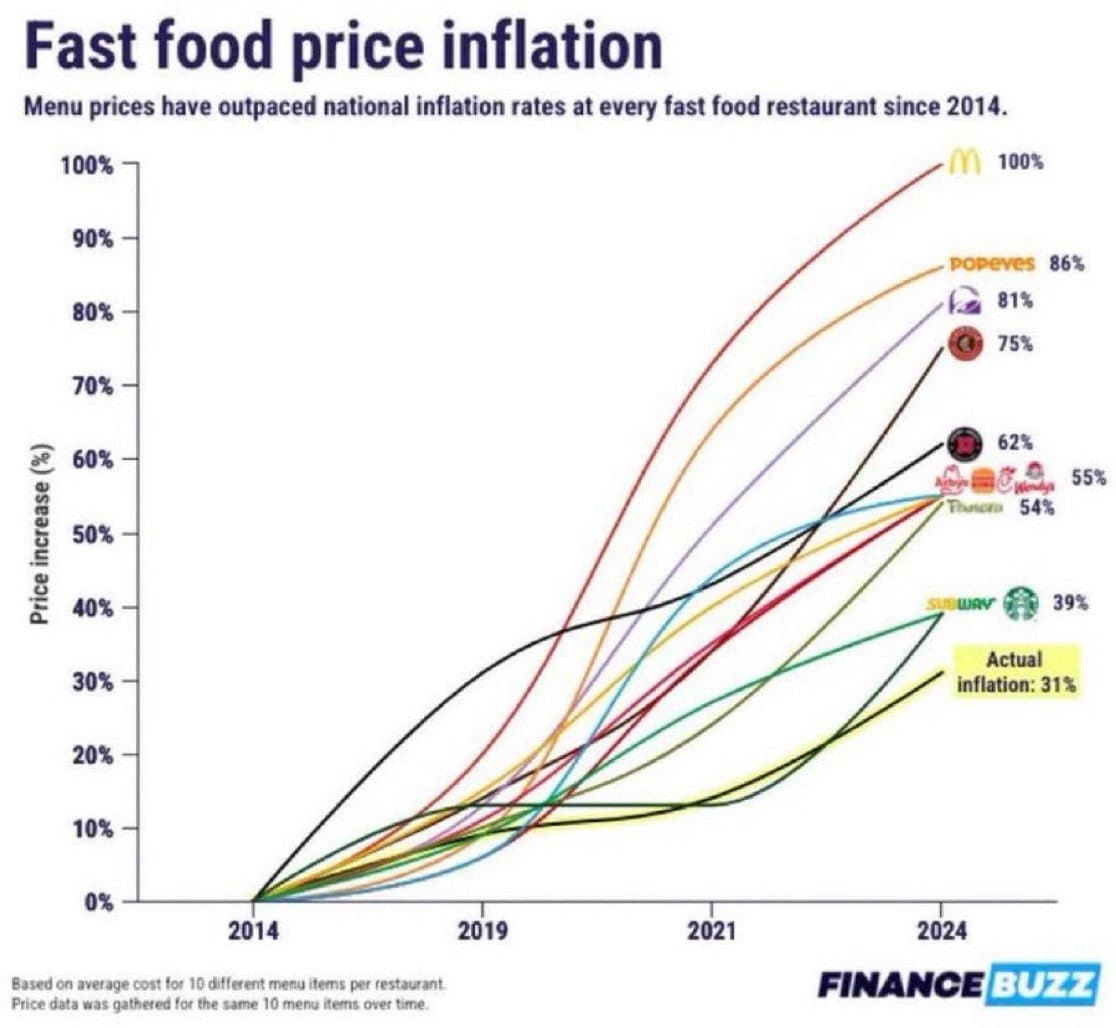
Fast-food prices in the United States have surged between 54% and 100% over the past five years, despite the official inflation rate remaining below 3%, as reported on September 4, 2025. This significant increase in fast-food costs has left many consumers questioning the sustainability of their food budgets.
The rise in prices has been attributed to a combination of factors, including increased labor costs, supply chain disruptions, and rising ingredient prices. Many fast-food chains have adjusted their menu prices to keep pace with these escalating expenses, leading to noticeable increases at the register for customers across the nation.
Historically, fast-food prices have been relatively stable, but recent trends indicate a shift. For instance, a popular burger chain has reported that the price of its signature burger has nearly doubled since 2020. This sharp increase stands in stark contrast to the overall economy, where inflation rates have been kept in check, leading to confusion among consumers who expect similar price stability across all sectors.
The implications of these price hikes are significant. With many families relying on fast food for convenience, the increased costs could lead to changes in consumer behavior, pushing them towards more affordable dining options or home-cooked meals. As previously reported, economic pressures continue to mount on American households, highlighting the need for a closer examination of food pricing amidst broader economic trends.






![[Video] Gunfire between Iraqi security forces and Sadr militias in Baghdad](/_next/image?url=%2Fapi%2Fimage%2Fthumbnails%2Fthumbnail-1768343508874-4redb-thumbnail.jpg&w=3840&q=75)
