India"s reliance on crude oil imports remains a pressing concern as a recent report highlights the irreplaceable role of Russian oil in the country"s energy landscape. Despite ongoing geopolitical tensions and sanctions against Russia, Indian refiners continue to prioritize Russian crude, underscoring the complexities of global oil markets. This article delves into the current state of India"s oil imports, the implications for energy security, and the broader geopolitical ramifications.
Background & Context
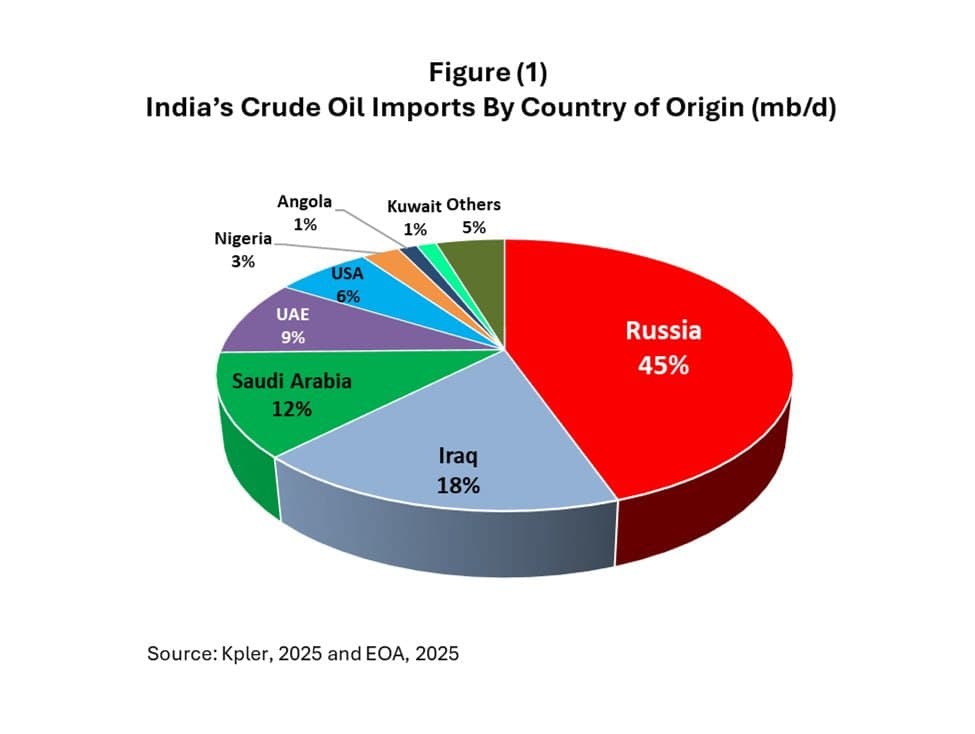
India"s energy consumption has surged in recent years, driven by rapid economic growth and urbanization. As the world"s third-largest oil importer, India is heavily dependent on external sources to meet its energy needs. In 2022, approximately 85% of India"s crude oil was imported, with Russia emerging as a significant supplier following the onset of the Ukraine conflict. The shift towards Russian oil has been a contentious issue, raising questions about energy security and geopolitical alignment.
Historically, India has diversified its crude oil imports, sourcing from countries like Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the United States. However, the current geopolitical climate has made it increasingly difficult to find viable alternatives to Russian crude, which is not only competitively priced but also readily available in the market. This situation has been compounded by the sanctions imposed on Russia by Western nations, which have inadvertently made Russian oil more attractive to countries like India.
Key Developments
Recent reports indicate that Indian refiners are set to increase their imports of Russian crude oil, despite the risks associated with doing so. For instance, data shows that in September 2023, Russian oil constituted nearly 40% of India"s total crude imports, a striking increase from the previous year. Industry analysts suggest that this trend is likely to continue as Indian refiners seek to capitalize on discounted prices following Western sanctions against Russia.
Notably, major Indian oil companies have reaffirmed their commitment to Russian crude, with some executives stating that there is "no viable replacement" for the supply. This sentiment reflects a broader acknowledgment within the Indian oil industry that while alternatives exist, they may not be economically feasible in the current market. As a result, Indian refiners are navigating a complex landscape, balancing economic interests with geopolitical considerations.
Broader Impact
The implications of India"s reliance on Russian oil extend beyond economic factors. Geopolitically, this dependence has positioned India in a precarious situation, particularly in its relations with Western nations. As India continues to import Russian crude, it risks alienating key allies who have imposed sanctions on Moscow. This complex dynamic has prompted discussions about India"s foreign policy and its desire to maintain strategic autonomy amidst global pressures.
Moreover, the increasing share of Russian oil in India"s energy mix has raised concerns about energy security. Experts argue that over-reliance on a single supplier can expose India to market volatility and geopolitical risks. As previously reported, similar situations have unfolded in the past where geopolitical tensions have disrupted oil supplies, highlighting the need for a more balanced approach to energy sourcing.
What"s Next
Looking ahead, the trajectory of India"s crude oil imports will largely depend on the evolving geopolitical landscape and market dynamics. Analysts predict that Indian refiners will continue to explore avenues for diversification, but the immediate future suggests a sustained dependence on Russian oil. In response to potential backlash from Western allies, India may seek to enhance its diplomatic engagements, balancing its economic needs with its geopolitical ambitions.
Additionally, as global oil prices remain volatile, India may consider investing in alternative energy sources and technologies to mitigate risks associated with oil dependency. The government"s push for renewable energy could gain momentum as it seeks to reduce reliance on imported crude. As the situation unfolds, stakeholders in the energy sector will closely monitor developments, navigating the intricate web of economic interests and geopolitical realities.






![[Video] Gunfire between Iraqi security forces and Sadr militias in Baghdad](/_next/image?url=%2Fapi%2Fimage%2Fthumbnails%2Fthumbnail-1768343508874-4redb-thumbnail.jpg&w=3840&q=75)
