Texas Data Centers Projected to Consume 399 Billion Gallons of Water by 2030 Amid Ongoing Drought
As Texas grapples with persistent drought conditions, a startling new report indicates that the state’s burgeoning data center industry could significantly impact its already strained water resources. A white paper set to be released by the Houston Advanced Research Center (HARC) reveals that data centers in Texas are expected to consume an estimated 49 billion gallons of water by 2025, with projections soaring to 399 billion gallons by 2030. This alarming figure represents approximately 6.6% of the total water usage across the state.
Background & Context
The impact of drought in Texas is not new; in fact, even after recent heavy rains, nearly a quarter of the state remains in drought conditions. The increasing demand for water from data centers highlights a growing tension between technological advancement and environmental sustainability. Most data centers utilize evaporative cooling systems to manage the heat generated by their servers. This method involves using water to absorb heat, which is then lost to the atmosphere through evaporation. As the water cycles through this process, it becomes saltier and unusable after just a few cycles, necessitating the disposal of vast quantities of water down the sewer.
Given the scale of water consumption projected for the future, experts are raising concerns about the sustainability of such practices, especially in a state that has historically struggled with water management. As previously reported, the balance between economic growth and environmental conservation continues to be a pressing issue for Texas policymakers.
Key Developments
The findings from HARC underscore the urgency of addressing water usage in sectors that have traditionally been overlooked. Mace, a representative from HARC, emphasized the critical nature of this issue, stating, “The water loss is significant, especially considering our current drought conditions.” With data centers proliferating in Texas, particularly in areas like Austin and Dallas, the demand for cooling water is expected to escalate dramatically in the coming years.
As technology companies increasingly establish operations in Texas, the question arises: how will the state manage the growing water needs of this industry? The projected rise in water usage raises alarms not only for local communities but also for agricultural sectors that rely heavily on consistent water supplies. The implications of this trend could be far-reaching, affecting everything from crop yields to municipal water availability.
\n\n
Image for Texas Data Centers Projected to Consume 399 Billion Gallons of Water by 2030 Amid Ongoing Drought
Broader Impact
The implications of this water consumption extend beyond immediate resource concerns. As Texas faces the dual challenges of climate change and a growing population, the pressure on water resources is anticipated to increase. Experts worry about the potential for conflict over water rights, particularly as urban areas expand and industries like data centers vie for limited supplies. The situation mirrors other regions facing similar challenges, where economic development often comes at the expense of environmental health.
In addition to the economic implications, there is a growing public awareness and concern regarding the environmental footprint of data centers. Many communities are beginning to push back against the unchecked expansion of these facilities, demanding more responsible water management practices. As seen in related coverage of recent developments in environmental policy, there is a growing call for legislative action to ensure that industries contribute to sustainable water management efforts.
What"s Next
Looking ahead, Texas lawmakers and industry leaders will need to engage in critical discussions about sustainable practices in water usage. Potential solutions may include investing in advanced cooling technologies that reduce water consumption or implementing stricter regulations on water use for data centers. As the white paper is released, it is expected to spark further debate and prompt stakeholders to explore collaborative approaches to manage water resources effectively.
As the situation evolves, the balance between fostering technological innovation and ensuring environmental sustainability will remain a pivotal challenge for Texas. With the projected water consumption of data centers looming large on the horizon, proactive measures will be essential to safeguard the state’s water resources for future generations.
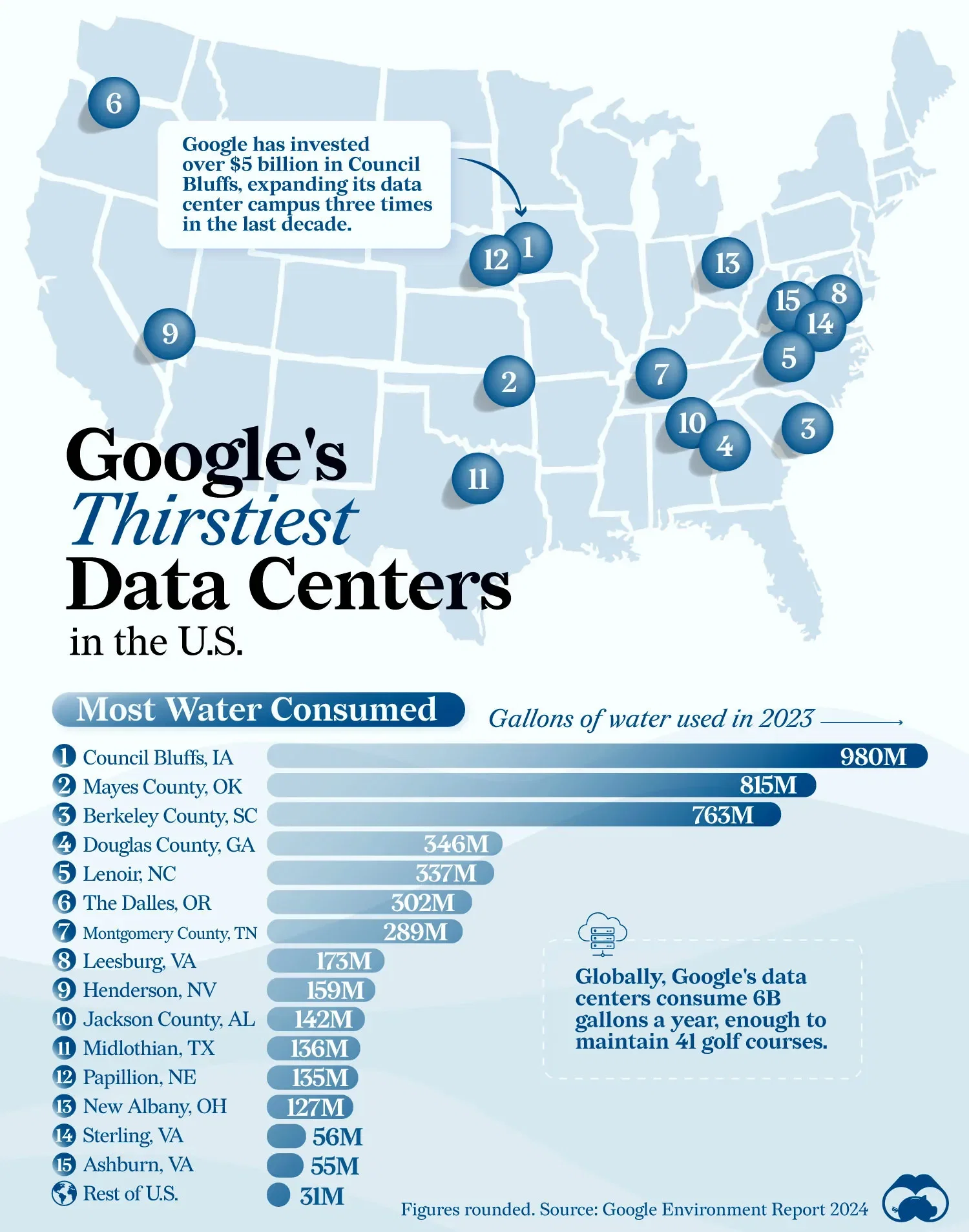
Image for Texas Data Centers Projected to Consume 399 Billion Gallons of Water by 2030 Amid Ongoing Drought



![[Video] Mount Etna erupts in Sicily, lava reaches 400 meters, yellow alert issued](/_next/image?url=%2Fapi%2Fimage%2Fthumbnails%2Fthumbnail-1766917884234-2sqn18-thumbnail.jpg&w=3840&q=75)
![[Video] Hawaii's Kilauea volcano erupts, fountains reach 70 ft, USGS reports](/_next/image?url=%2Fapi%2Fimage%2Fthumbnails%2Fthumbnail-1766574042820-tucull-thumbnail.jpg&w=3840&q=75)


![[Video] Gunfire between Iraqi security forces and Sadr militias in Baghdad](/_next/image?url=%2Fapi%2Fimage%2Fthumbnails%2Fthumbnail-1768343508874-4redb-thumbnail.jpg&w=3840&q=75)
