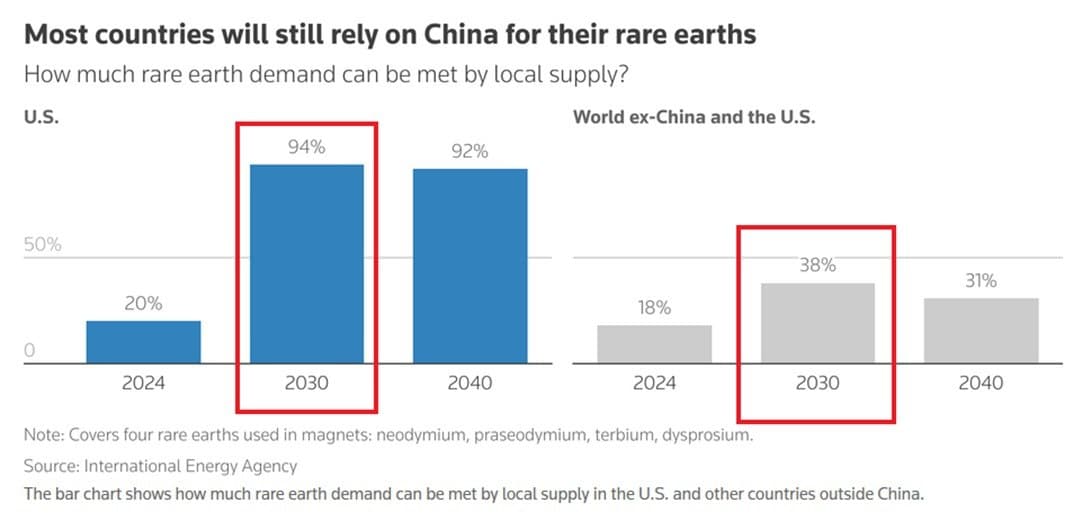
US to Meet 94% of Rare Earth Demand Domestically by 2030, Down from 20% in 2024
According to a recent report by Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, the United States is poised to significantly reduce its reliance on China for rare earth elements, a critical component in various high-tech applications. By the year 2030, the US is expected to meet approximately 94% of its rare earth demand from domestic sources, a substantial increase from just 20% in 2024. This shift is part of a broader strategy to enhance domestic production capabilities amid growing concerns over supply chain vulnerabilities and geopolitical tensions.
Key Details
The report highlights that while the US is making strides in domestic production, Western economies will still depend heavily on China for the processing of heavy rare earths. Specifically, it is projected that China will account for 91% of heavy rare earths processing through 2030, albeit a decrease from 99% in 2024. This indicates a slow but steady diversification of supply sources among Western nations.
In terms of global supply, China is anticipated to supply around 60% of the world"s rare earth elements that are essential for the production of high-performance magnets by 2030. This statistic underscores China"s dominant position in the rare earth market, despite the efforts of other countries to bolster their own production capabilities.
In contrast to the US"s projected increase in domestic sourcing, the rest of the world is expected to meet only 38% of its rare earth demand locally by 2030, a notable rise from 18% in the previous year. This disparity highlights the varying levels of progress among different regions in establishing self-sufficient supply chains for these critical materials.
Background
Rare earth elements are a group of 17 chemical elements that are vital for the manufacturing of a wide range of products, including electronics, renewable energy technologies, and military applications. The increasing demand for these materials has raised concerns about over-reliance on China, which has historically dominated the rare earth supply chain. The US government has recognized the strategic importance of securing a stable supply of rare earths and has initiated various measures to enhance domestic production.
Efforts to increase domestic production include investments in mining and processing facilities, as well as partnerships with private companies and research institutions. The US aims to not only reduce its dependence on foreign sources but also to create jobs and stimulate economic growth within the country.
What"s Next
The projected increase in domestic rare earth production in the US signals a significant shift in the global supply chain landscape. As the US moves towards meeting 94% of its rare earth demand domestically by 2030, it will likely influence global market dynamics and encourage other nations to pursue similar strategies. The ongoing developments in the rare earth sector will be closely monitored, especially as geopolitical tensions continue to shape trade relationships.
For further context on related geopolitical developments, readers may refer to recent developments in the Middle East and how they may impact global trade.
As the rare earth market evolves, stakeholders from various sectors will need to adapt to the changing dynamics, ensuring that they remain competitive in an increasingly interconnected global economy.






![[Video] Gunfire between Iraqi security forces and Sadr militias in Baghdad](/_next/image?url=%2Fapi%2Fimage%2Fthumbnails%2Fthumbnail-1768343508874-4redb-thumbnail.jpg&w=3840&q=75)
